Why Rest And Recovery Are Important For Athletes
Rest and recovery are arguably the most important activities for any athlete (of any skill level). How you spend your downtime between workouts and your quality of sleep is the foundation of a healthy mind and body.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 1 in 3 adults in the United States reported not getting enough rest or sleep. Evidence suggests sleep deficiency can lead to physical and mental health problems, injuries, impaired quality of life, and loss of productivity.
Athletes who don’t get enough (quality) sleep are more prone to:
Delayed reaction time
Decreased performance
Injuries
Reduced stamina
Getting sick
Difficulty making decisions
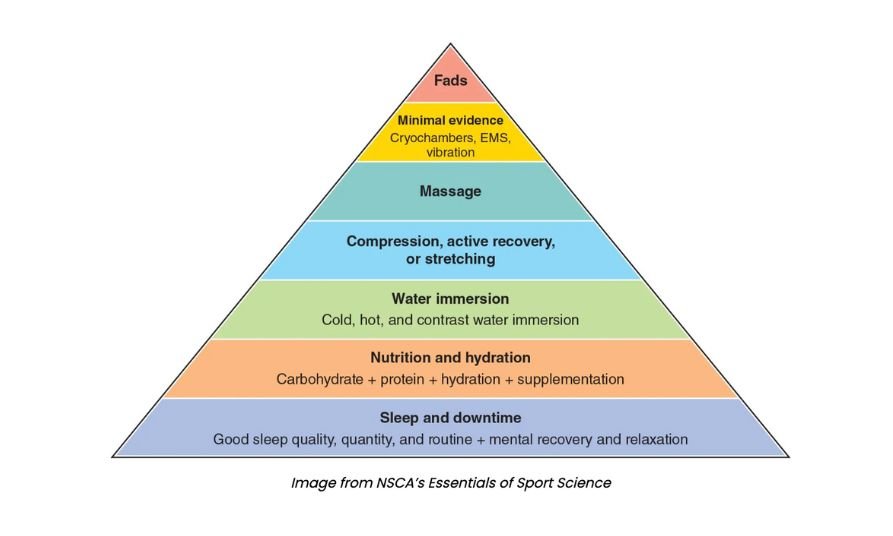
Let’s review the recovery pyramid below. As you can see, it’s built on the foundation of sleep, followed by nutrition and hydration. These three areas have the greatest impact on athletic performance. Sleep helps recover and re-energize the brain and muscles, which is why the quality of sleep is widely used as a measure of performance for all athletes, no matter the sport.
The primary difference between athletes and non-athletes is that athletes undergo more physical and physiological stress consistently. Making it essential for athletes to incorporate physical and mental downtime. Sleep naturally takes care of both. The National Sleep Foundation recommends the following amount of sleep:
Athletes (of all ages) 7-9 hours;
Adolescents 8–10 hours;
Adults 7–9 hours; and
Older Adults 7–8 hours.
Of course, the amount of sleep is not the only factor in a good night’s sleep; the quality is too. The following factors improve sleep quality:
Follow a sleep schedule (i.e., going to bed at the same time every night and waking up at the same time every morning);
Practice relaxing routines before bedtime;
Sleeping on a supportive and comfortable mattress and pillow;
Create an optimal sleeping environment (minimize light and sound and optimize the temperature);
Monitor your intake of caffeine and alcohol before bed; and
Disconnect from all electronic devices 30 minutes before bedtime.
The best way to tell if your body is getting enough sleep is by taking a full-body assessment. Schedule your consultation today to check if you are at the optimal level of your performance..